Citation
Michie, K. A., Litfin, T., Beecroft, S. J., Collins, B., Czabotar, P., Downton, M., Doyle, M. T., Ghosal, D., Grinter, R., Knott, G. J., Samaha, G., Christiansen, J. H., & Gustafsson, O. J. R. (2025). Australian Structural Biology Deep-Learning Infrastructure Roadmap. Zenodo. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.15786982
Executive Summary from roadmap
Enabled by advances in deep learning methods for protein structure prediction and de novo protein design, computational structural biology has rapidly emerged as a powerful technology driving innovation in both fundamental and translational science. The technology underpins breakthroughs in drug design, diagnostics, personalised medicine, and synthetic biology. However, effective use requires concentrated interdisciplinary expertise and access to modern graphics processing unit (GPU) hardware that few Australian researchers or industry can sustain. The Australian structural biology community has taken a collaborative approach to develop this infrastructure roadmap which describes the existing national landscape, identifies and prioritizes critical research bottlenecks, and proposes a national strategy to unlock the immense potential of computational structural biology for Australian researchers. This strategy is intended to evolve as the requirements of the community change. The roadmap outlines the challenges faced but also presents opportunities to maximize the value of this new technology. A robust, sovereign capability in computational structural biology and protein design will position Australian universities, research institutes, and industry at the forefront of global innovation.
The community roadmap outlines 4 major deliverables including:
- D1. A dedicated community space to foster collaboration and share best-practice recommendations for software deployments, benchmarking, validations and insights developed within the community.
- D2. Community training resources to on-board diverse stakeholders within the context of computational structural biology and strengthen the national impact of community expertise.
- D3. National computational infrastructure built on increased hardware investment and a user platform to facilitate efficient, high-throughput utilization of national computing resources and drive translational outcomes enabled by curated and validated computational structural biology technologies.
- D4. Alignment, integration and engagement with global best-practice efforts for computational structural biology infrastructure and research.
Achieving these outcomes will not only enable the community to add value across diverse research disciplines within Australia, but will drive innovation and enhance the national research and enterprise profile in medicine and biotechnology on the global stage.
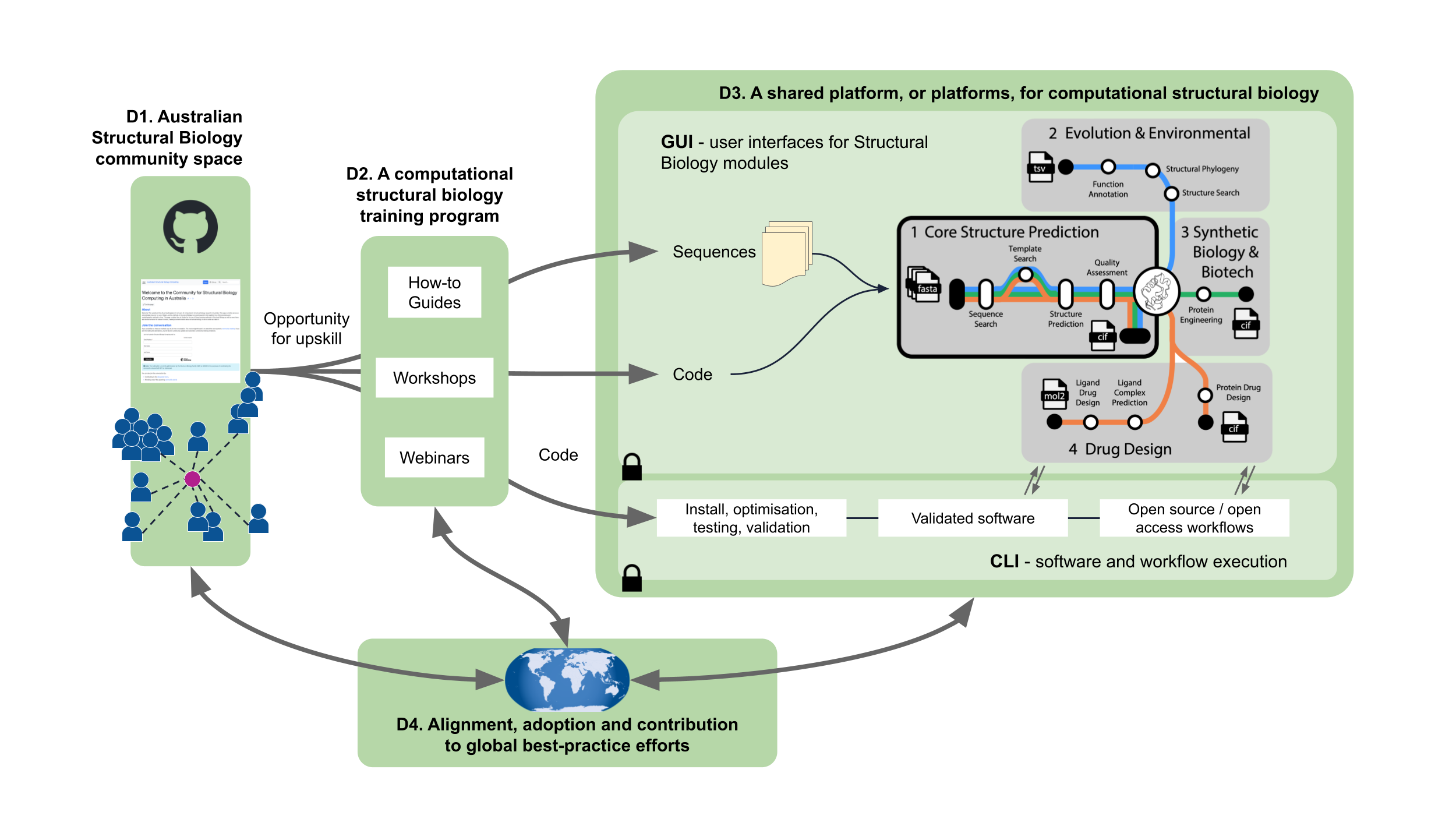
Roadmap Figure 3. Proposed infrastructure to support Australian structural biology computation: (D1) Australian Structural Biology community space. (D2) Tailored training program connects the proposed infrastructure to the BioCommons training program and includes community generated guidance material. (D3) Shared platform, or platforms, for computational structural biology. Protein sequences, or other relevant sequence data (e.g. nucleotide), as well as code, are inputs into the envisaged hypothetical shared platform for computational structural biology analyses, which provides both command-line interface (CLI) or graphical user interface (GUI)-based access to validated software tools and workflows. This system is underpinned by sufficient and appropriate computational infrastructure. (D4) Alignment to international best practice highlights the aim to align, adopt and collaborate with international peer infrastructures to deliver the proposed infrastructure. Arrows indicate the general flow of data. See Appendix 1 for a list of open source tools / workflows that may be included in D3. Globe image: Clker-Free-Vector-Images, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons.
Completed
- Initial draft of infrastructure roadmap.
- Initial community feedback incorporated, content updated, implementation section added.
- Review and updates based on feedback from co-authors and academic panel.
- Review and updates based on feedback from community and BioCommons infrastructure partners.
- Review and updates based on feedback from international experts.
- Addressing final review comments.
- Publication to Zenodo.
Contributors
- Australian Structural Biology Computing Community
- Australian BioCommons and infrastructure partners